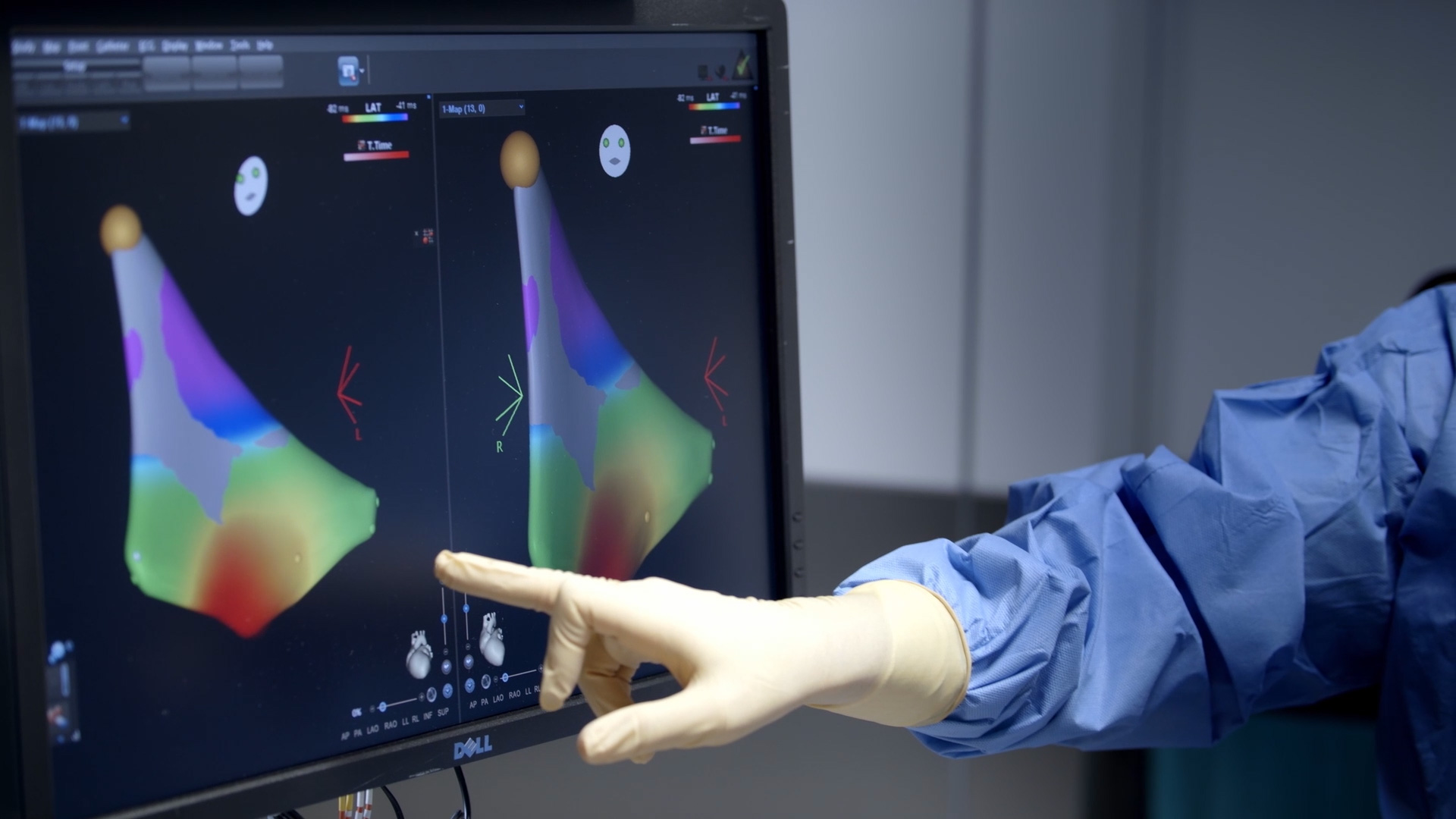
Shock, horror, uncertainty - a diagnosis of cardiac arrhythmia in children causes many strong emotions in young patients and their relatives. However, cardiologists reassure: successful treatment of heart rhythm disorders, also for the youngest patients, is possible. Ablation, a chance for a healthy and active life for children with heart rhythm disorders, is the subject of a new educational campaign, 'Action Ablation - Children'.
Shocking diagnosis
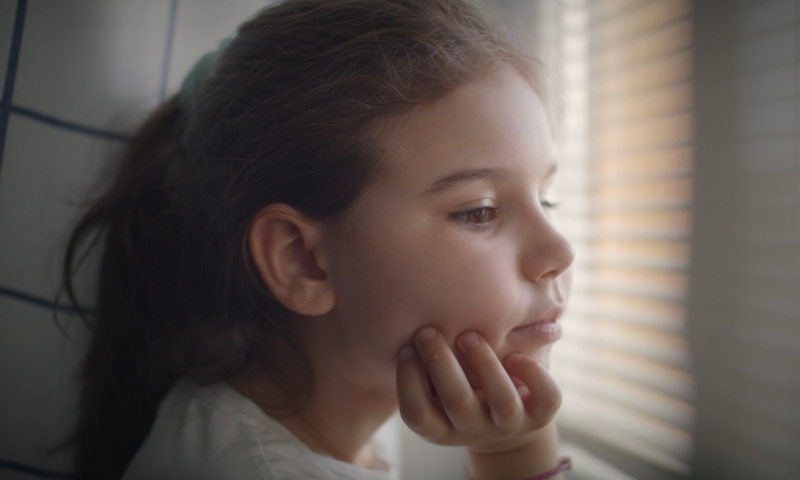
Blanka is a smiling, healthy newborn. At least, that's how it seems. Until the parents notice some worrying symptoms in their child: Blanka tires faster than her peers, her heart seems to be working somehow... strangely. Mr and Mrs Solnica feel that something is wrong with their baby. They decide to visit the doctor, who, however, does not suspect anything worrying. The parents don't give up: they keep a watchful eye on their daughter and continue to consult doctors. When the girl's condition suddenly deteriorates, the parents go to see another specialist. The specialist diagnoses that there is something wrong with Blanka's heart. We have to go to hospital immediately!
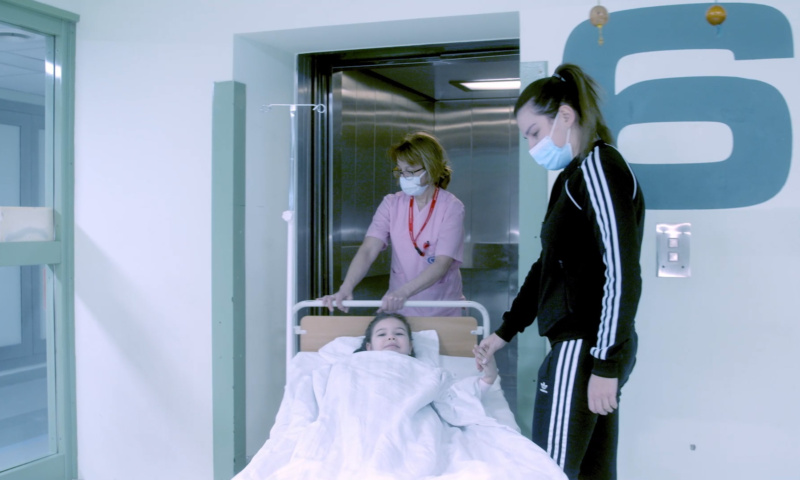
In a hospital in Lublin, a girl is taken to the ICU. Doctors save her life and diagnose: it's a dangerous heart rhythm disorder: supraventricular tachycardia. The family is devastated and terrified: what does the diagnosis of arrhythmia mean for our child? Does Blanka have a chance to live a normal life? Fortunately, it turns out that successful treatment and a return to daily activities are very much possible.
- Blanka's arrhythmia diagnosis came as a shock to our whole family. We didn't know what it entailed, what to expect, what the further life of our daughter would be like. Fortunately, after emergency intervention in a hospital in Lublin, we were taken under further specialist care by wonderful doctors from the Children's Health Centre in Warsaw. There everything was calmly explained to us. It turned out that effective treatment was possible in our Blanka's case. They explained to us what the next stages of treatment would look like. It was no longer completely 'black magic' for us. This knowledge helped us a lot," says Emilia Solnica, Blanka's mother.
Knowledge is support!
For the benefit of children and parents in a similar situation, the Solnic family decided to share their story. They want to support others during the difficult stages of arrhythmia diagnosis and treatment, to show that an initially frightening story can have a happy ending. This is the aim of the educational campaign 'Ablation Action - Children', organised by the Heart for Arrhythmia Foundation.
- As part of the new iteration of our 'Action Ablation' campaign, we use accessible, colourful animation, a video vlog and interviews with experts to explain what heart rhythm disorders occurring in children entail and what the whole treatment pathway for a young patient might look like. We focus not only on the medical side, but also on the emotional side. We were supported by paediatric cardiologists specialising in electrophysiology, i.e. the diagnosis and treatment of arrhythmias. These specialists are well aware of the specific problem of arrhythmia in the youngest patients. Their knowledge and guidance will certainly be of great help to many people in a situation similar to that of the Solnic family," declares Jakub Zawadzki, president of the "Heart for Arrhythmia" Foundation.
A like arrhythmia
- Arrhythmia, or cardiac arrhythmia in other words, is generally when the patient's heart does not work as it should. Arrhythmias can be asymptomatic and harmless, but there are also dangerous, even fatal arrhythmias - especially if they are of a certain type and are not recognised in time. It is because of these that so-called sudden cardiac deaths occur. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is the most common cause of cardiac arrhythmias in children. The child experiences these as palpitations. Sometimes this is a very difficult symptom for the young patient - both physically and emotionally. Fortunately, various arrhythmias can now be treated very effectively," says Maria Miszczak-Knecht, MD, PhD, from the Cardiology Clinic at the Children's Memorial Health Centre in Warsaw, national consultant in paediatric cardiology.
Depending on the individual indication, arrhythmias can be treated by pharmacological (drugs) or surgical methods, including ablation. The method that is used if a patient at risk of sudden cardiac death has to be protected is the implantation of a cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD). For many arrhythmias, lifestyle modification of the patient is no less important than properly managed therapy. According to specialists, changing daily habits brings a significant gain in terms of reducing the number of arrhythmia attacks.
Action: ablation!
In Blanka's case, it was decided that the most effective and optimal treatment would be with an ablation procedure for the underlying arrhythmia. This is a method that is also used in adult patients with certain heart rhythm disorders. In the youngest patients, this procedure proceeds in almost the same way as in adults, with the exception that in children general anaesthesia is used (the child is asleep during the procedure).
- During the ablation procedure, electrodes are inserted into the patient's heart. Their function is to record the heartbeat, and they can also be used to create a three-dimensional map of the patient's heart. This allows us to find the source of the arrhythmia and then target the therapy exactly there. The treatment consists of delivering radiofrequency energy of a specific power to specific points in the heart via radiofrequency conducting electrodes. The aim is to neutralise the foci of arrhythmia in the patient's heart. The first effects of the treatment can be felt immediately after the procedure, but it is necessary to wait up to several weeks for the full effect of the therapy. This is the amount of time it takes for the tissues responsible for the abnormal conduction of impulses in the heart to be fully 'neutralised' - this process is gradual," explains Maria Miszczak-Knecht, MD.
After the procedure, the patient stays under the control of the attending centre. If everything is fine, he or she only comes in for regular, scheduled check-ups for two years. This is the case for Blanka.
Living - to the full!
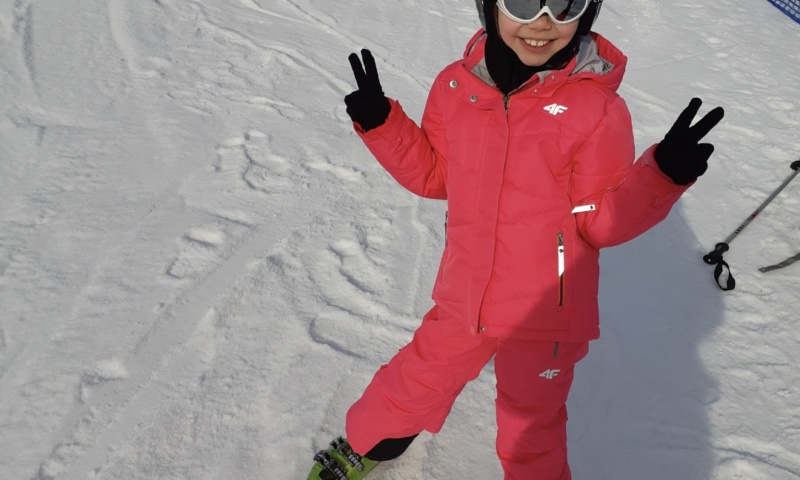
- When playing, I sometimes get tired, but not as much as I used to anymore. Today I can play normally with my friends and my dog, running, jumping, doing flips. It's great! - declares the girl.
According to the national consultant in cardiology, ablation is an opportunity for a complete cure and a full return to health and daily activity for many patients with arrhythmias.
- The detection of an arrhythmia in a child should prompt the child's siblings, as well as the parents, to be examined as well. First of all, an ECG should be evaluated. The family history is important: have relatives had a history of loss of consciousness and sudden death before the age of 50? For the safety of the whole family, this is worth checking," says Dr. Maria Miszczak-Knecht, MD.
The website of the educational campaign 'Action Ablation - Children': http://dzieci.akcjaablacja.pl/
Site of the educational campaign 'Action Ablation', aimed at adult patients: https://www.akcjaablacja.pl/
For more information about the Heart for Arrhythmia Foundation: https://www.sercedlaarytmii.pl/